What is a smart home? It’s a home equipped with connected devices—lighting, thermostats, security cameras, locks, speakers, appliances, and more—that you can control remotely or automatically to save time, energy, and hassle. In 2024, smart homes are a rapidly growing reality worldwide, but not without important cautions and limitations worth knowing right now.
Key Takeaways
- Smart home adoption is booming globally and regionally, but user frustrations and costs are often underreported.
- The biggest markets are North America, Asia Pacific, and Europe, but Africa and Latin America are catching up as smart tech gets cheaper.
- Security, privacy, and real user pain points deserve close attention before investing in smart home automation.
The Core Concept
A smart home is a home equipped with internet-connected devices that automate and remotely control key functions—like lighting, temperature, entertainment, cleaning, and security—either through smartphones, voice assistants, or scheduled routines. Smart home technology aims to simplify daily life, improve comfort, optimize energy usage, and boost security for homeowners.
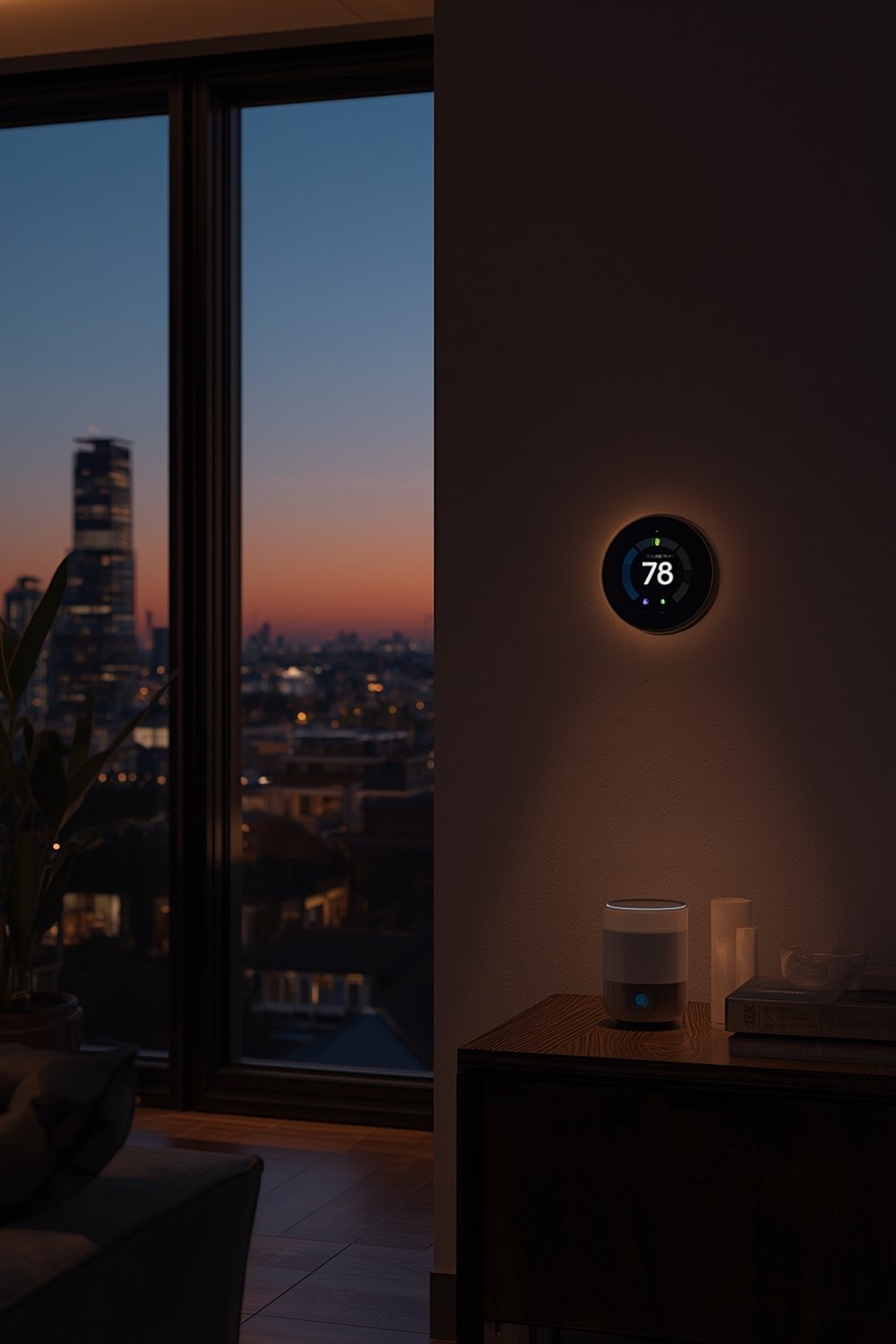

Why does it matter? Smart home adoption is no longer a futuristic luxury. By the end of 2024, there are 422 million users worldwide. The market’s total value now spans from $127.67 billion to $154.4 billion, with some projections as high as $537 billion by 2030 (source) (source 2). What’s changed is that smart devices—once a novelty—are now found in everything from lighting to robot vacuums for pet hair and smart locks. Advanced features like learning thermostats, voice control, and real-time alerts set smart homes apart from conventional “dumb” devices.
Regions differ in adoption:
- North America: 41% U.S. households use smart home tech, with the highest average home spend ($479.70 per smart home).
- Asia Pacific: Fastest growth, led by China, India, and the Far East.
- Europe: Prioritizes energy-efficient and secure automation, high penetration projected to reach 48% plus by 2028.
- Africa/Middle East & Latin America: Smaller share, but significant growth as urbanization increases.
Smart homes are everywhere—with smart alarm clocks, AI-powered pet care, and even smart kitchens—but real-world results aren’t always as seamless as they look in advertising.
Step-by-Step Guide
Ready to make your home smarter? Here’s how to get started with smart home automation—no hype, just clear steps:
- Decide what you want to automate first. Focus on a single pain point: do you want easier security, energy savings, cleaner floors, or hands-free lighting? Prioritize 1-2 rooms or routines, like installing a smart thermostat for temperature control or an upgraded video doorbell for front porch security.
- Pick a platform (ecosystem). Most smart homes revolve around a hub or app, like Amazon Alexa, Google Home, or Apple HomeKit. Make sure your chosen devices are compatible before buying. Consider future upgrades, especially if you plan to add smart lighting, cleaning robots, or Homebridge for third-party compatibility.
- Set a realistic budget. Average revenue per smart home in 2024 is about $365 globally. Actual costs vary: basic setups can start at $100-$300, while whole-home systems (with multi-room controls) can exceed $1,000 plus. There are ongoing fees for subscriptions, device replacements, and—sometimes—professional installation.
- Install your first device and connect it. Start with something standalone—like a smart bulb, plug, or security camera. Follow app instructions and manufacturer setup steps precisely. Test manual and app-based controls. Many products have clear, step-by-step setup wizards or QR code scanning to simplify the process.
- Expand gradually and integrate with routines. Once you’re comfortable, group devices into automations or “scenes.” For instance, you could have all lights turn off at bedtime or set the vacuum to clean after you leave (see robot vacuum reviews for options).
- Regularly update and maintain your devices. Vendors push updates for new features and critical security fixes, so enable auto-update when possible. Reboot or re-pair devices if they become unreliable.

Want inspiration? Check out recommended smart home products spanning cleaning, lighting, security, and pet care to match your needs and budget.
Advanced Analysis & Common Pitfalls
Smart homes offer real benefits—but also reveal a range of practical challenges and pitfalls, especially after installation. While top-ranking articles promote market boom and user numbers, recent research highlights key gaps few discuss:
- Reliability and Compatibility: Many users face glitches—devices drop from WiFi, schedules fail, or different brands don’t work together seamlessly. Hybrid protocols help, but not every device supports them (source).
- Missing Real-World Reviews of User Frustrations: 2024 research finds almost zero published surveys on post-setup smart home pain points. However, forums and anecdotal reports often cite steep learning curves, spotty automation, and confusion over data privacy.
- Security and Privacy Risks: Security and access control devices make up almost 30 percent of the smart home market. There’s growing demand for trustworthy systems, particularly in Europe—but very little information on recent vulnerabilities, or what’s being done to fix them (see here).
- Hidden Costs: While global average revenue per smart home is $365.60 (source), actual prices span basic $20 gadgets to multi-room packages costlier than standard appliances. Ongoing support, cloud subscriptions, and professional installs can add up quickly.
| Aspect | What Top Articles Say | What’s Missing or Underexplained |
|---|---|---|
| User Challenges | High adoption, seamless experience | No survey data on real frustrations after setup |
| Security & Privacy | Security is a leading product segment | Lack of specifics on hacks, fixes, or transparent privacy approaches |
| Costs | Average annual spend is quoted | No itemized breakdowns for device, installation, or ongoing fees |
| Platform Comparison | Mentions Alexa, Google, Apple frequently | No head-to-head comparisons, protocol confusion, little on third-party integration |
| Measurable Benefits | Energy efficiency is a common claim | No published user-reported savings numbers or long-term benefit evidence |
If you’re researching specific products—like a non-toxic air fryer for the kitchen or a bouclé bed frame for a smart bedroom—dig into user reviews and third-party forums. Marketing claims alone rarely reveal everyday glitches, privacy trade-offs, or how robust integrations actually are.

Conclusion
Smart home automation is quickly becoming the standard around the globe, powered by maturing technology, falling costs, and consumer demand for convenience. But rapid growth means new users face real world trade-offs: unclear security updates, uneven device integration, and hidden long-term costs. Before investing, use this resource as a checklist for realistic planning, platform comparison, and maintenance. If you need practical starter picks or want to build a truly smart kitchen or bedroom, check out our best product picks and recommendations.
Ready to make your home smarter? Learn more or start building your layered automation setup—just keep in mind all the facts outlined in what is a smart home today.
FAQ
What devices make up a smart home?
Common smart home devices include lighting, thermostats, security cameras, video doorbells, smart locks, plugs, garage controllers, cleaning robots, alarm systems, appliances, and speakers. They connect over WiFi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, or multiple protocols for centralized control.
How much does it cost to set up a basic smart home?
Entry-level systems (like a few bulbs or plugs and one voice assistant) can start at $100-$300. Full setups with multi-room hardware, cameras, and professional installation can reach $1,000 plus. Ongoing costs include replacements, subscriptions, and possible professional support.
Are smart homes really secure in 2024?
Security has become a top product concern, but actual risks and vulnerabilities are rarely detailed in market reports. Always keep devices updated, use strong WiFi passwords, and stick to reputable brands. Research shows demand for better security, especially in Europe and North America.
Which smart home platform is the best?
No single platform fits all. Alexa, Google Home, and Apple HomeKit each offer strengths, but compatibility, app design, and integration with third-party devices vary widely. Research your current/future device needs and check if bridges or hubs like Homebridge are required.
Can smart home tech actually lower my energy bills?
Many smart home marketers claim energy savings, especially for smart thermostats and adaptive lighting. While market growth is driven by energy efficiency demand, there’s little published user data with exact savings or ROI numbers. Individual results depend on use case and device setup.